Millis Delay Example For Arduino
What is delay () ?
We all
are familiar with delay() function in Arduino. For example
delay(1000) will give a 1 second delay to the program code. The
major disadvantage of this function is that it will pause the entire
code from execution. The delay() function is known as 'Code Blocking'. What it
does is pauses the code for a set amount of time. The time it pauses for is
indicated within the brackets in milliseconds. Eg: delay(1000) will
pause the code for 1 second. This will affect some large code
execution when some sensors or LCDs are interfaced.
Here comes the
concept of millis delay function. The
millis() function is nothing
like delay(). It helps us time events without pausing the code. The Arduino Reference
for millis() says it: Returns
the number of milliseconds passed since the Arduino board began running the
current program.
How To Use millis() Instead of delay()?
After reading above,
we have covered why and when you should use millis(), and now we get to the
all-important how. How to use millis() to time your events instead of using
delay() to pause your events.
Instead of pausing
your program, what you need to do is write a small equation to check if the
correct amount of time has passed, if the correct amount of time has passed, do
the event, or else keep looping.
Let's rewrite the
'Blink' project, and convert it from using delay() to using millis(). After
this code, we will break down what is going on.
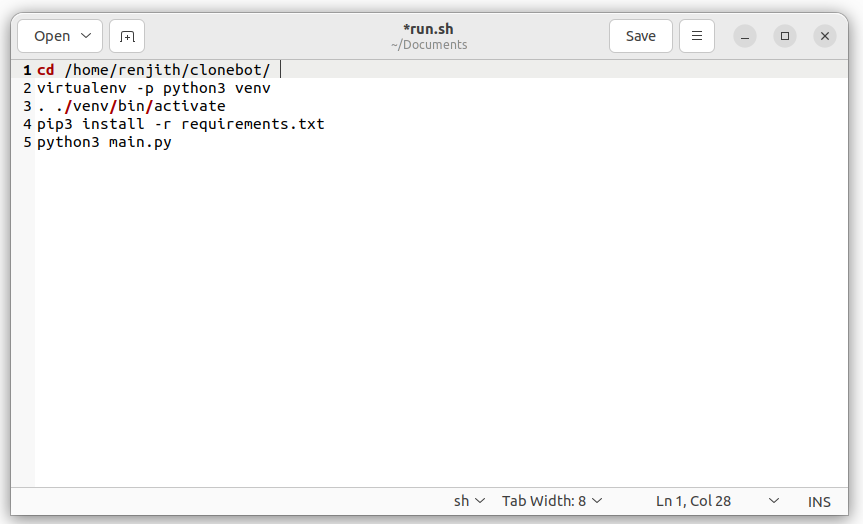
Here is one example which gives 1
second (1000 microseconds) delay using millis delay. Basically Pin number 13 of
Arduino has connected an in built led. The programme blinks the above led.
Please refer through the code. I have used millisDelay.h library to write
the code. For more about the library and syntax, visit here.
Code :
#include <millisDelay.h>
int LedPin = 13; //Inbuilt Led is assigned
millisDelay TimeDelay;
bool LedOn = false;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
TimeDelay.start(1000); //Give 1 second delay
pinMode(LedPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop(){
if (TimeDelay.justFinished()) {
TimeDelay.repeat();
LedOn = !LedOn;
if (LedOn) {
digitalWrite(LedPin, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(LedPin, LOW);
}
}
}

Comments
Post a Comment